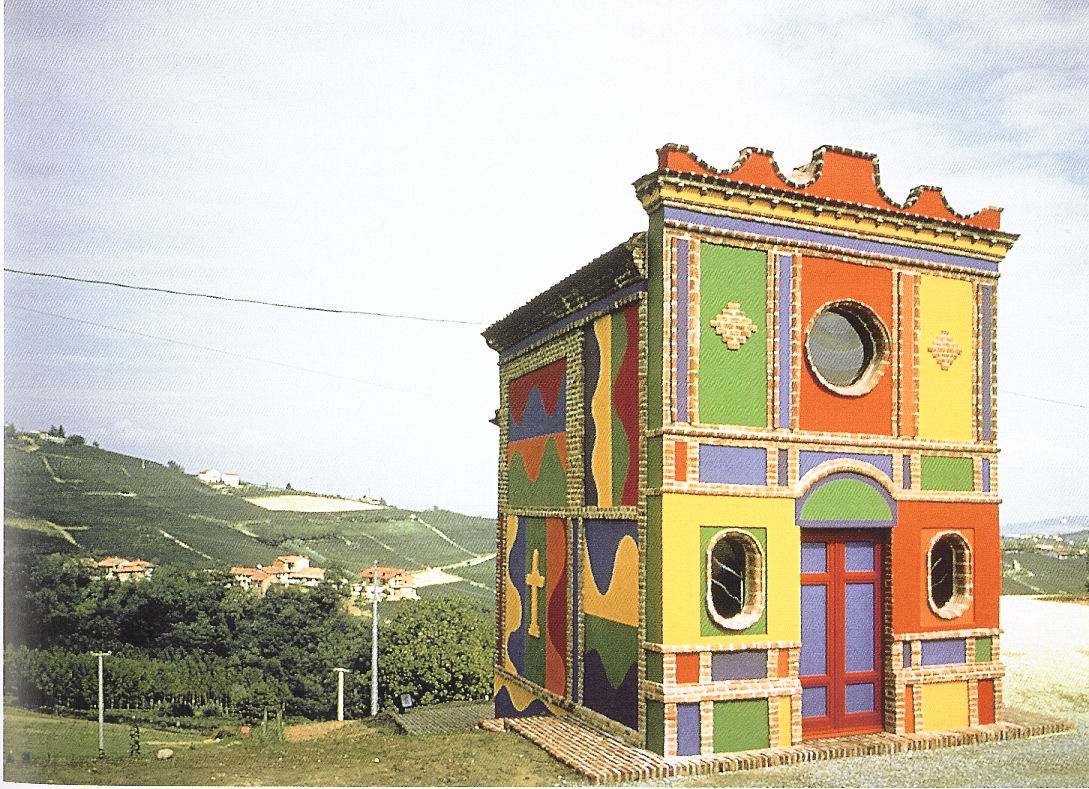
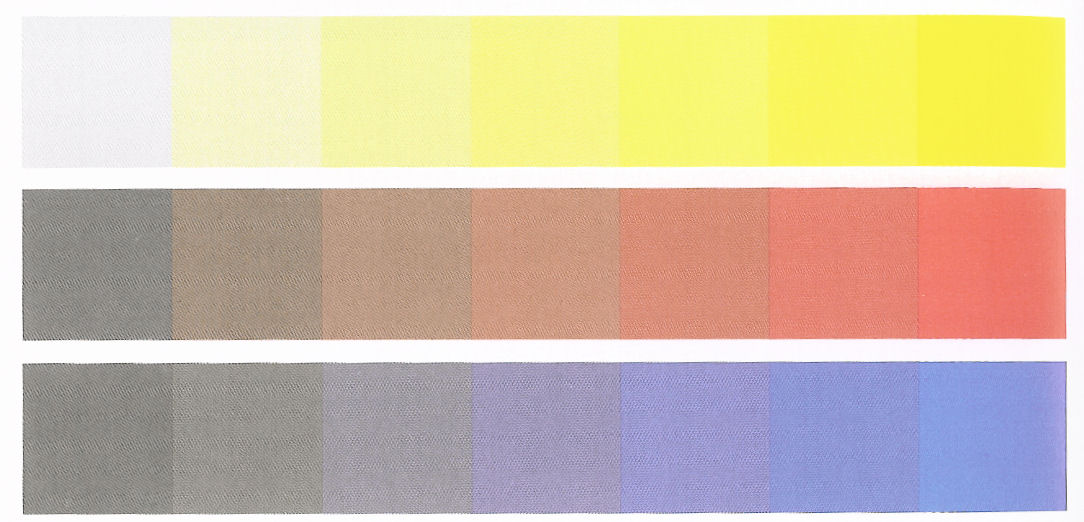
Color
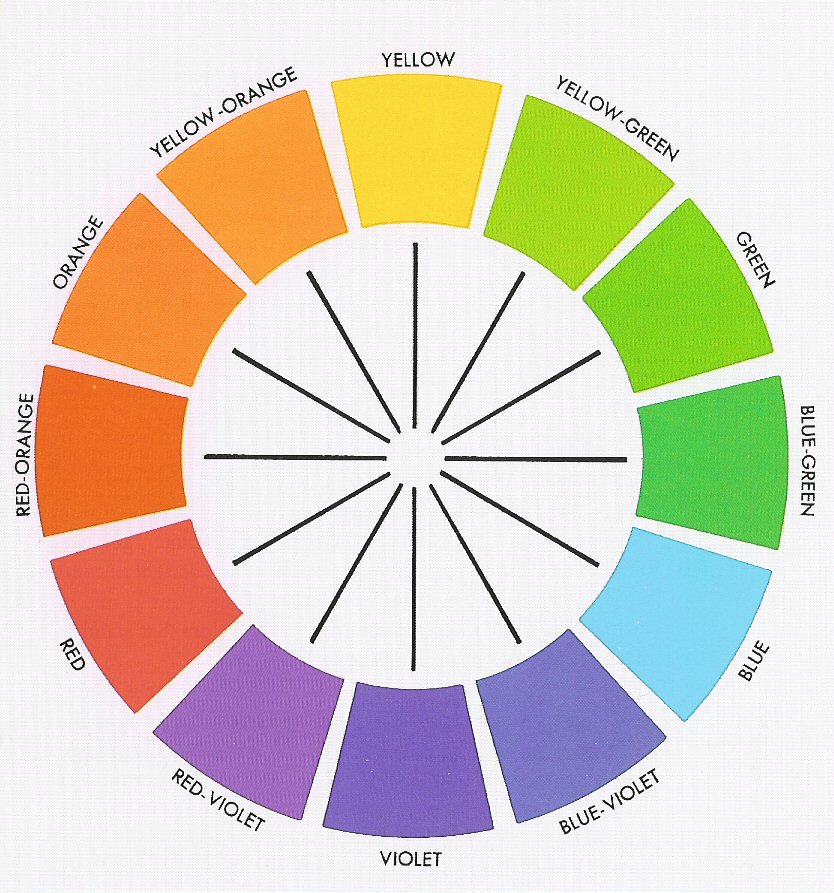
Color Wheel (based on Sir Isaac Newton, "Opticks" 1692)
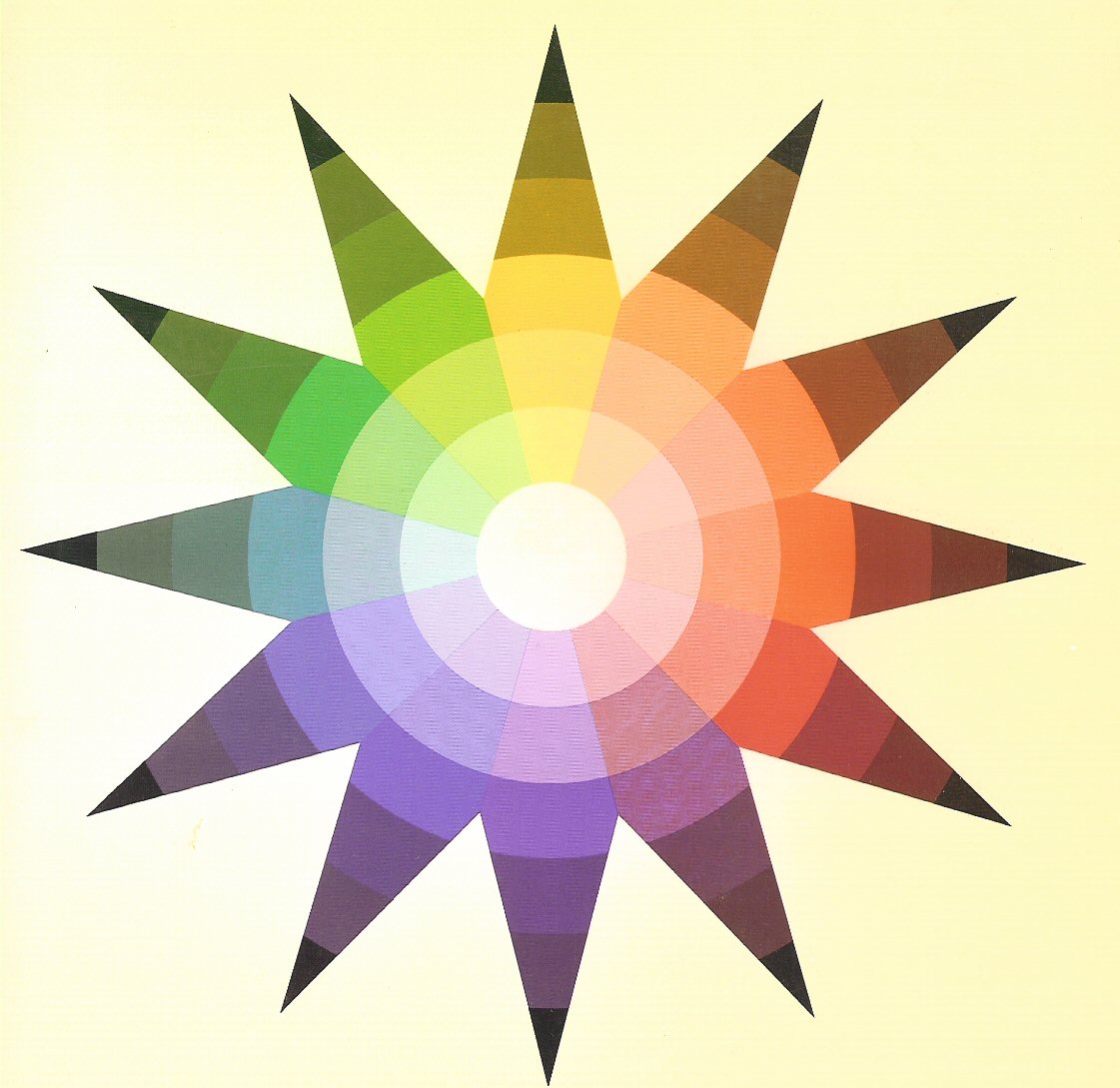

Color Star
(developed by Johannes Itten ca. 1950 at the Bauhaus
and published in The Art of Color, 1970)
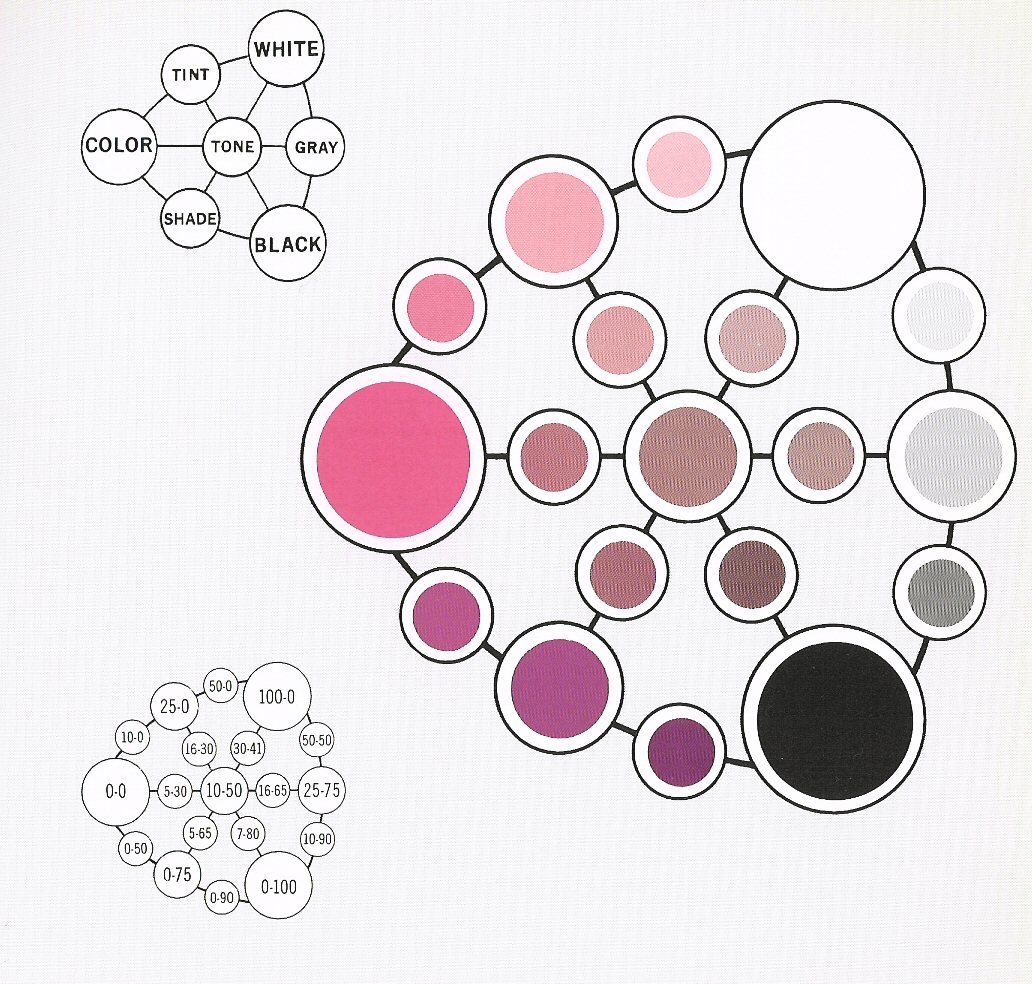
Tints and Tones
Munsell Color Notation
System
In the Munsell system of notation, color characteristics are designated by three axes - hue (the name of the color), value (the darkness or lightness of the color), and chroma (the intensity, or strength of the color). A color could be called 5R 5/12, which means, the middle hue of red, a value of 5 which is halfway between white and black, and a chroma of 12 which is as strong as red can be. In this system, there are 10 basic hues, and 10 sub-steps, giving a total of 100 visual hues.
The system was developed by American painter Albert Henry Munsell (1858-1918) in his book A Color Notation, in 1905. Today, the Munsell color system is available as color chips through GretagMacbeth AG with main offices in Switzerland.
Click here to link to Munsell color system web site
Another system for organizing colors is the Plochere Color System, which was developed in 1948 in accordance with the Nobel prize-winning Latvian/German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald's (1853-19323) color theory, which was an outgrowth of Munsell's. Today the Plochere company sells color chips.
Click here to link to the Plochere color system web site
Another common color system has been developed by the Pantone company, located in Washington, USA.
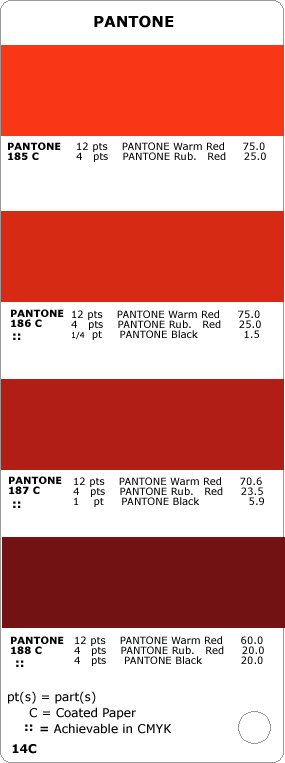
Pantone Color Guide (sample page) - contains 1114 colors with Pantone numbering system