- Purpose of the building foundation: carry building loads to the ground
- Types of foundations
- Continuous spread footings
- Piers and grade beams
- Piles and grade beams
- Caissons and grade beams
- Raft (4' to 8' thick reinforced concrete slab)
- Floating (weight of earth excavated = total building load)
- Basement is designed like a truss
- Foundation must be rigid
- Soils
- Surface of earth is overlaid with:
- Bedrock (The Teton Mountains are exposed bedrock, for example)
- Water
- Unconsolidated material (soil) formed by disintegration of bedrock
- "Undisturbed" soil
- "Organic" materials (dead animals or plants)
- Fill
- Engineered fill
- Soil classification
- Granular (grain size classification by USDA)
- Sand: 1/5000" to 1/500" in diameter
- Gravel: greater than 1/12" in diameter
- Cohesive
- Silt: 1/12500" to 1/5000" in diameter
- Clays: less than 1/12500" in diameter
- Organic (not suitable for foundations)
- "Black dirt" (it is great for growing crops in, though)
- "top soil"
- peat
- loam
- Design of footings based on allowable soil pressures
- Allowable soil pressures
- Determined by testing - taking "borings" on the site
- Typical range from 2000 to 6000 pounds per square foot (psf)
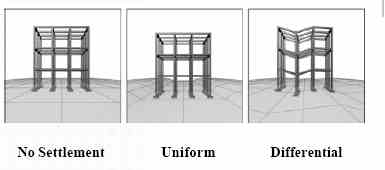
- Settlement
- Settlement is normally expected
- Maximum of 1" settlement is typical
- Consistency of settlement is desirable
- Causes of settlement
- Reduction of volume of voids in the soil
- Lowering of the water table
- Rupture of the soil
- Lateral displacement (sliding)
- Compression of the grains
- Frost heave
- "Frost line" - 3'-6" below grade in most areas around Chicago (Note: some suburbs of Chicago require minimum depth of foundations to be 4'-0" below grade)
- "Frost walls" for light loads such as porches, stoops, or fence walls.
- Stoop arms
- Water table
- Moisture in soil between grains
- Ground water level
- Trapped water (perched water tables)
- Dewatering during construction
- Dangers of lowering water table
- Dampproofing of foundations
- Sub-soil drains
- Waterproofing of foundations
- Ventilation of basements and crawl spaces
- Purposes of ventilation
- Basements: 2% of floor area
- Crawl spaces
- Without vapor retarder: 1/150 of crawl space area
- With 6 mil polyethelene vapor retarder: 1/1500
of crawl space area
-
Site Preparation
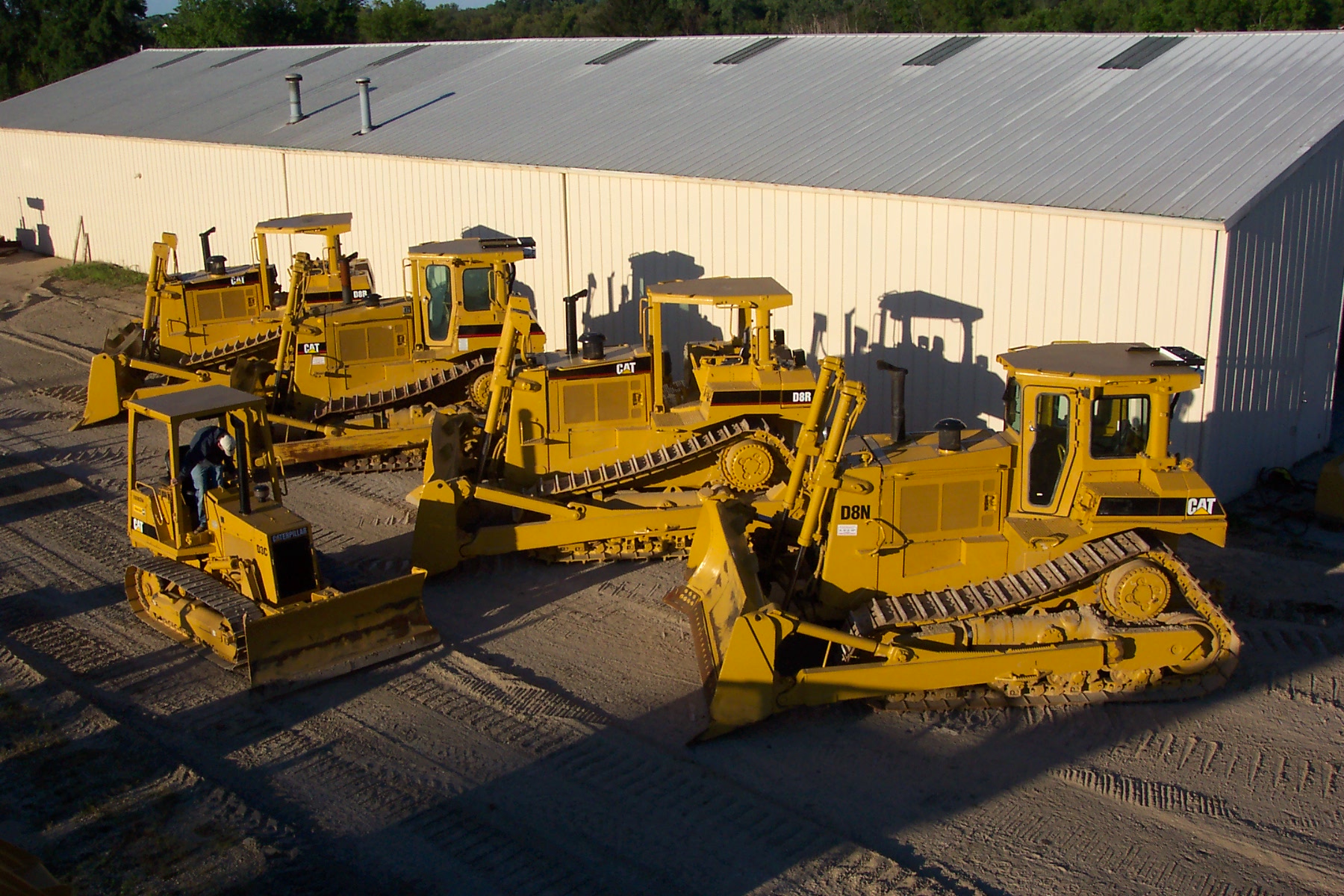
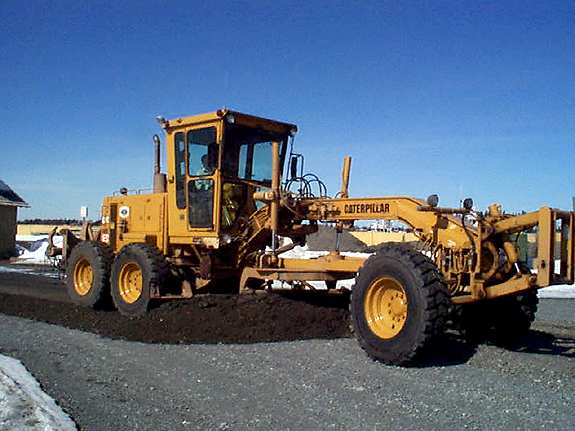
Equipment used

-
Bulldozers

-
Grader

-
Front end loaders

-
Hydraulic excavator

- Back Hoe

14. Skid Steer Loader

15. Wheel Loader