Module 21 - Operant Conditioning
§ type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment
- Law of Effect
- Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely
Types of Behavior
- Operant Behavior
- operates (acts) on environment
- produces consequences
- Respondent Behavior
- occurs as an automatic response to stimulus
- behavior learned through classical conditioning
B.F. Skinner (1904-1990)
- elaborated Thorndike’s Law of Effect
- developed behavioral technology
- Skinner Box
- chamber with a bar or key that an animal manipulates to obtain a food or water reinforcer
- contains devices to record responses
Reinforcer
- any event that strengthens the behavior it follows
- Shaping
- operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer approximations of a desired goal

Principles of
Reinforcement
- Primary Reinforcer
- innately reinforcing stimulus
- i.e., satisfies a biological need
- Conditioned Reinforcer
- stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with primary reinforcer
- secondary reinforcer
Schedules of
Reinforcement
- Continuous Reinforcement
- reinforcing the desired response each time it occurs
- Partial (Intermitent) Reinforcement
- reinforcing a response only part of the time
- results in slower acquisition
- greater resistance to extinction
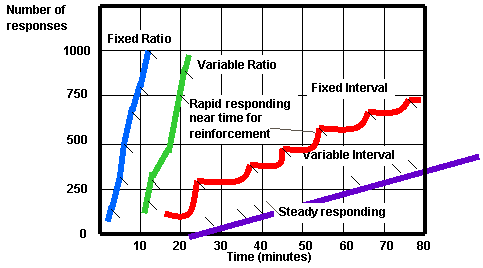
- Fixed Ratio (FR)
- reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses
- faster you respond the more rewards you get
- different ratios
- very high rate of responding
- like piecework pay
- Variable Ratio (VR)
- reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses
- average ratios
- like gambling, fishing
- very hard to extinguish because of unpredictability
- Fixed Interval (FI)
- reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed
- response occurs more frequently as the anticipated time for reward draws near
- Variable Interval (VI)
- reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals
- produces slow steady responding
- like pop quiz
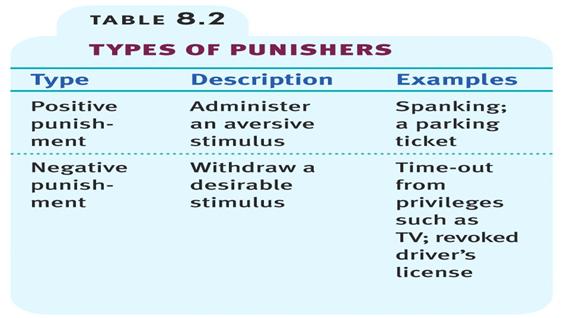
Punishment
- aversive event that decreases the behavior that it follows
- powerful controller of unwanted behavior
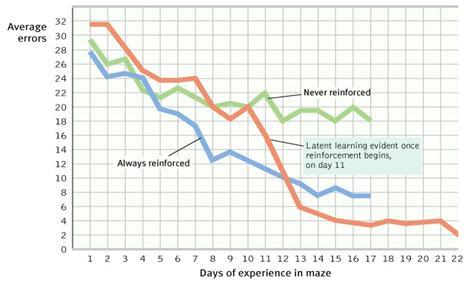
Cognition and Operant Conditioning
- Cognitive Map
- mental representation of the layout of one’s environment
- Example: after exploring a maze, rats act as if they have learned a cognitive map of it
- Latent Learning
- learning that occurs, but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it
Latent
Learning
Motivation
- Overjustification Effect
- the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do
- the person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest, as the motivation for performing the task
- Intrinsic Motivation
- desire to perform a behavior for its own sake and to be effective
- Extrinsic Motivation
- desire to perform a behavior due to promised rewards or threats of punishments
NOTE:
See: www.uwc.edu/OperantCon
- an interactive explanation of Reinforcement and Punishment, Positive and
Negative.